Digital Rights Management (DRM) is a critical technology that helps companies like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Hulu protect their digital content. If you've ever tried recording or downloading a Netflix video, you may have noticed that it's impossible. But how exactly does Netflix achieve this? Let's explore how DRM works, and the technical measures Netflix employs to prevent unauthorized downloads.
What is DRM?
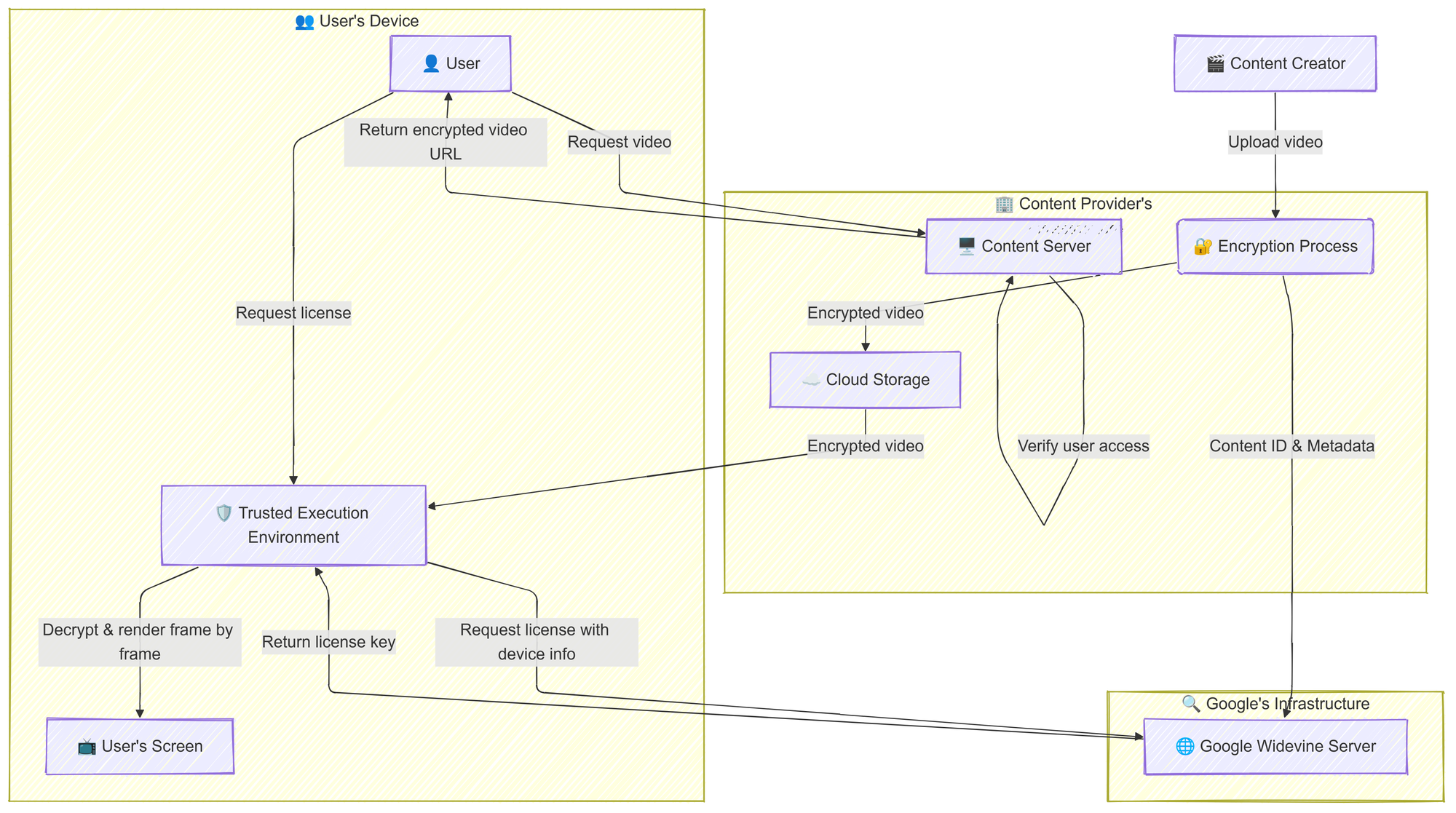
DRM stands for Digital Rights Management, a technology designed to protect digital content from piracy. It works by encrypting the content, making it playable only under certain conditions and on authorized devices. The primary purpose of DRM is to control how users' access, copy, and distribute digital content.
Netflix, Amazon Prime, Hulu, and other streaming services use DRM to ensure their content is protected. Even if a video is being streamed on your screen, DRM prevents you from downloading or recording it, providing a layer of protection for content creators and distributors.
The Basics of DRM: Encryption and Decryption
At the core of DRM is the process of encryption and decryption. Here's a simplified breakdown of how it works:
- Encryption: When a video is uploaded to a platform like Netflix, it's encrypted using algorithms like AES 128-bit encryption. This transforms the video file into a "garbage" format that can't be played unless decrypted.
- Keys for Decryption: To decrypt the file, two keys are required: an encryption key and an initialization vector (IV). The combination of these keys transforms the encrypted video back into a playable format.
- Clear Key Encryption: One of the basic DRM methods is Clear Key Encryption. In this case, the encryption key is transmitted to the user's device. While the video is encrypted, the decryption key is easily accessible, making it vulnerable to interception.
How Netflix Enhances DRM Security
Netflix uses more advanced forms of DRM than simple Clear Key Encryption to ensure that even tech-savvy users can't easily bypass the protections. Here's how Netflix goes beyond basic DRM:
- Widevine DRM: Netflix uses Widevine, a DRM scheme developed by Google, to enhance the security of its content. Widevine encrypts videos and requires a secure licensing server to verify user access and deliver encryption keys.
- Trusted Execution Environments (TEE): In certain cases, the decryption process is offloaded from the software level to a hardware-based Trusted Execution Environment (TEE). For example, when you play Netflix on Google Chrome, the highest resolution available is 720p. That's because Chrome does not trust hardware-level encryption. However, if you use Safari on macOS, Netflix allows 4K resolution because Apple’s hardware has secure TEE, making the decryption more secure.
- Device-Specific Decryption: Netflix tailors the encryption process to specific devices. You might notice that Netflix only plays in low resolution on certain devices, while others support higher resolutions. This restriction is because Netflix enforces a certain level of security to prevent high-quality pirated copies.
- Preventing Screen Recording: Netflix also employs techniques to stop users from recording content with screen capture software. When you try to record, the screen might turn black, and you can only hear the audio. This happens because the video playback is tightly controlled, and certain software can’t access the video content.
Why DRM Isn’t Foolproof
While DRM is an essential tool for preventing piracy, it's not perfect. A determined individual can still find ways to record or download DRM-protected content. For instance, someone could record their screen using a camera or find vulnerabilities in outdated DRM implementations.
There have been instances where DRM-protected content was hacked. For example, a bug in Chrome's DRM implementation in 2016 allowed hackers to intercept and download video streams directly. Though such vulnerabilities are patched over time, it's a constant battle between content providers and pirates.
DRM Beyond Netflix
DRM isn't exclusive to Netflix. It’s used in various industries, from online courses to software applications. For example, if you’re selling video courses online, you might want to prevent users from downloading or sharing them without permission. Services like Widevine and FairPlay (Apple’s DRM solution) are available for companies that want to protect their content. However, these services come at a cost and require a partnership with companies like Google and Apple.
Conclusion
DRM plays a crucial role in protecting digital content from piracy, but it's not without limitations. While Netflix and other platforms have sophisticated DRM systems like Widevine and FairPlay in place, these systems are continuously evolving to stay ahead of piracy attempts. As technology advances, so too will the methods for securing digital content.
In the meantime, the current DRM solutions used by Netflix ensure that only authorized users can access high-quality video content, preventing illegal downloads and protecting the interests of content creators.
